Projects
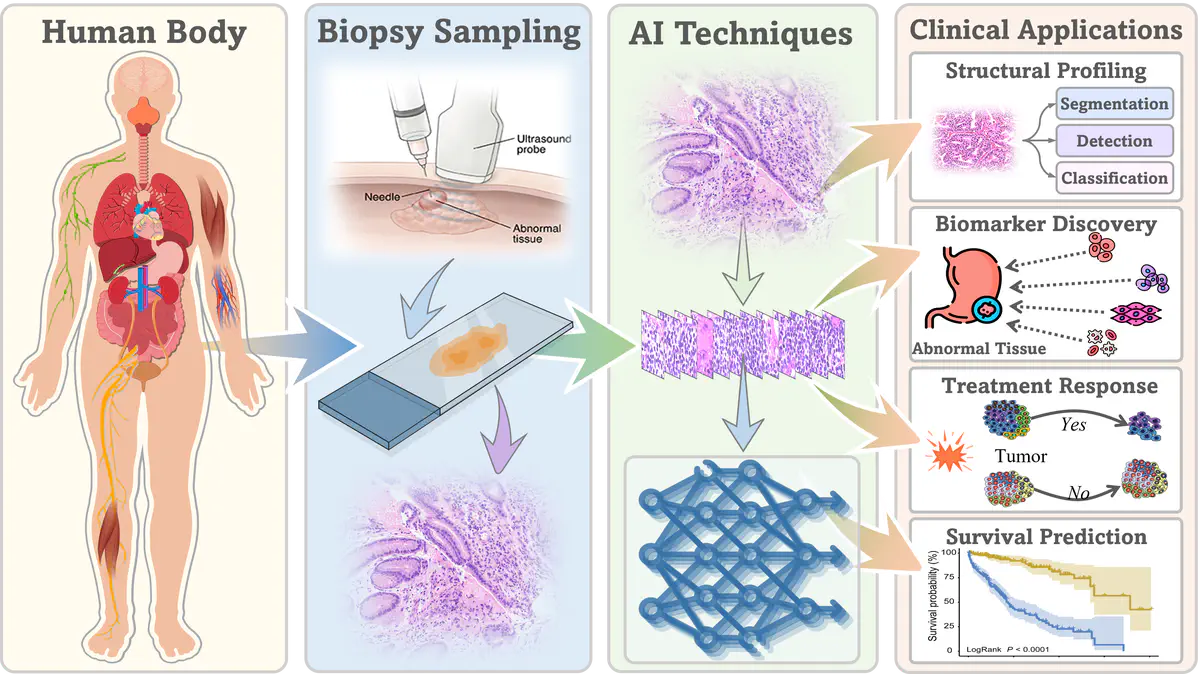
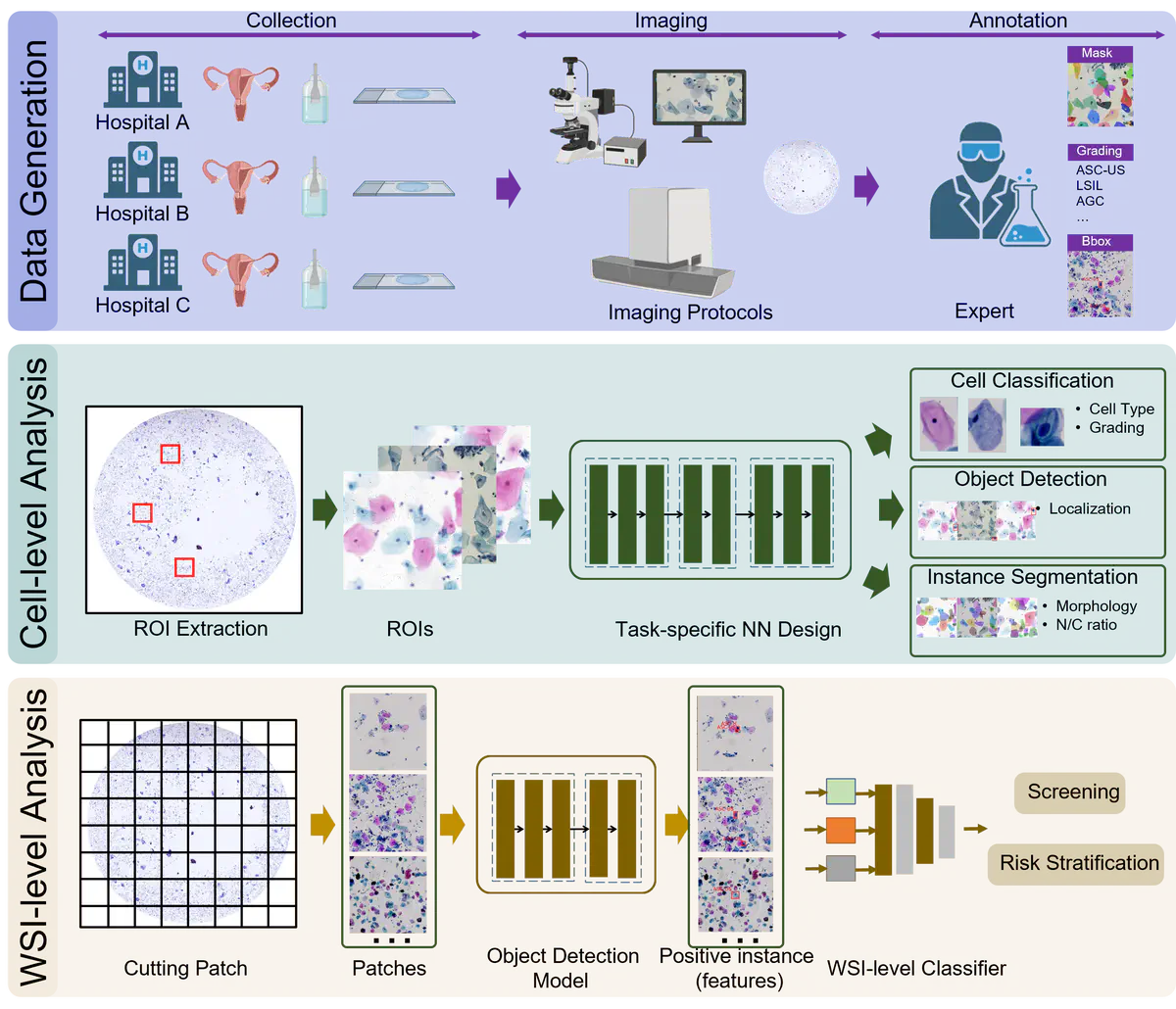
Computational cytology enables efficient and accurate cancer screening and early diagnosis such as liquid-based cytology in cervical cancer screening, reducing the heavy workload on cytologists by identifying the suspicious abnormal cells. In this project, we focus on building a deep learning assisted cytology analytical system and consequently predicting diagnostic outcomes. We will build a data standardization platform for specimen collection, imaging, and annotation. Furthermore, we will develop advanced deep learning algorithms for quantifying cell-level and whole slide image (WSI)-level analytical results. We aim to develop an integrated system for data acquisition, imaging analysis, visualization and human-machine collaboration.
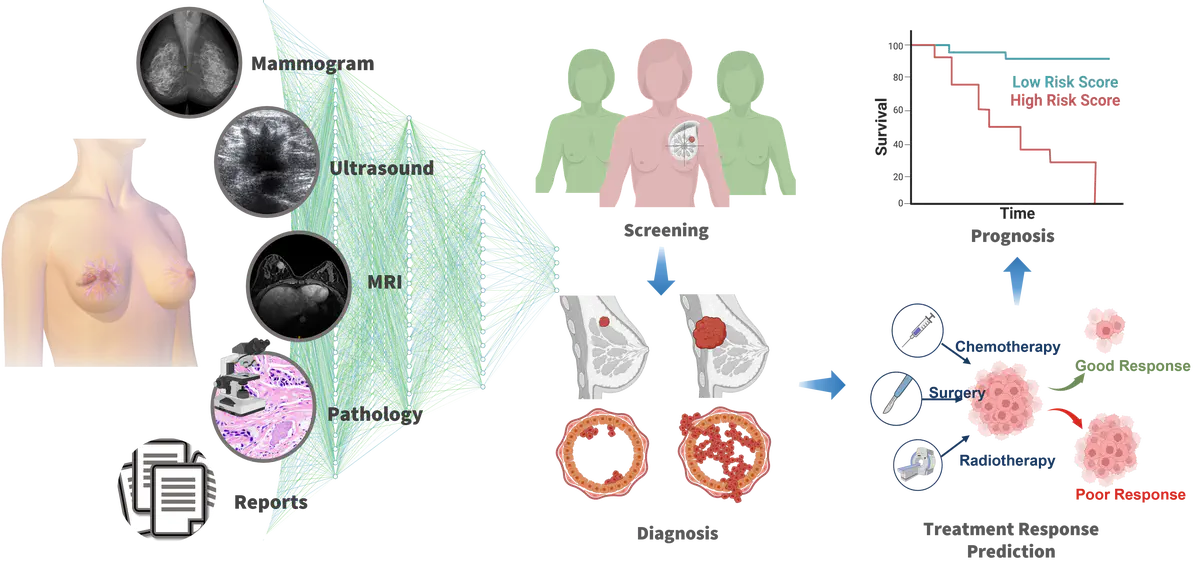
Breast cancer has become the most diagnosed malignancy worldwide and the primary cause of cancer mortality in women, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases and 685,000 deaths in 2020. Early screening and diagnosis of breast cancer can effectively improve the five-year survival rate of patients. Meanwhile, personalized neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) response prediction can reduce unnecessary suffering from toxic therapy and economic cost for patients who have poor responses. In this project, we aim to establish a deep learning-assisted system for breast cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment response prediction from multimodal data, so as to improve the diagnostic efficiency and accuracy of doctors while increasing the life quality of patients significantly via personalized treatment.